- Written by: Hummaid Naseer
- June 19, 2025
- Categories: Tech Stack
When developing a bespoke software solution, understanding the difference between frontend and backend is essential, not just for developers but also for clients. These two components work together to deliver the functionality and experience users expect. The frontend refers to everything users see and interact with directly, like buttons, forms, animations, and page layouts. It’s built using technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
On the other hand, the backend powers what happens behind the scenes, handling data processing, server logic, user authentication, and database management, often built with languages such as Python, Node.js, or Java.
Sometimes grasping this distinction helps set clearer expectations, budget wisely, and make more informed decisions during the planning and development stages. One common misconception is that a beautiful interface means the system is fully functional. However, without a solid backend, even the most polished UI is just a shell. Similarly, a powerful backend with no usable frontend fails to serve end users effectively.
What Is the Frontend?
Frontend development involves key technologies such as HTML (which structures the content), CSS (which styles it), and JavaScript (which adds interactivity). Modern frontend frameworks like React, Vue.js, and Angular make building dynamic and responsive user interfaces faster and more scalable.
Everything a user clicks, views, or types into, like buttons, navigation menus, forms, page layouts, images, and animations, is part of the frontend. For example, when you fill out a contact form, browse a product catalog, or toggle between light and dark modes on a site, you’re interacting with the frontend.
What Is the Backend?
Backend development involves technologies like PHP, Node.js, Python, and Java, alongside databases (such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB) and APIs that connect different systems or services. It’s the part of the software that processes user requests, stores and retrieves data, and ensures everything runs securely and efficiently.
Typical backend functions include user authentication (logins and permissions), order processing, data retrieval, form submissions, and server-side logic. For example, when a user logs into an app, the backend checks their credentials, fetches their data from the database, and delivers the correct response to the frontend.
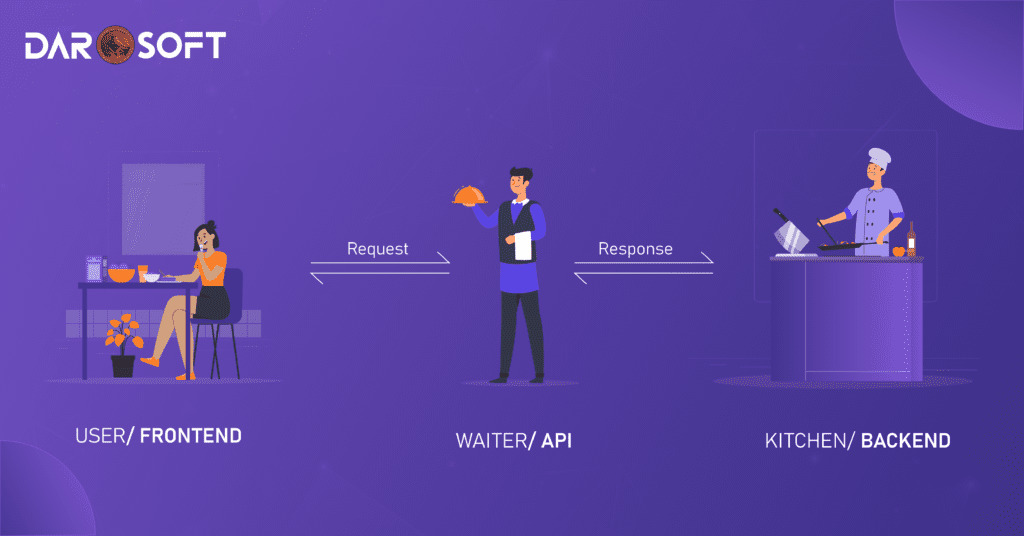
How Frontend and Backend Work Together: The request-response cycle
The frontend and backend work together through a request-response cycle to deliver a smooth and functional user experience. When a user interacts with the frontend, like submitting a form, the input is sent to the backend via an API, which acts as a bridge between the two. Think of an API like a waiter in a restaurant: the frontend (user) tells the waiter (API) what they want, the backend (kitchen) prepares the dish (data), and the waiter brings it back to the table. This helps different parts of the system communicate smoothly.
The backend then processes the data, performs any necessary actions (such as validation or database storage), and returns a response. The frontend then uses this response to update the interface, such as displaying a confirmation message. This seamless communication ensures that, while users only see the interface, the backend quietly powers everything behind the scenes.
Full-Stack Development: The Best of Both Worlds
Full-stack development involves handling both the frontend and backend of an application, making it ideal for projects that need speed and flexibility. Full-stack developers can build user interfaces and manage server-side logic, allowing for faster development, smoother collaboration, and fewer handoffs. This approach is especially valuable for startups and Minimum Viable Products (MVPs), where small teams and rapid iterations are essential for success.
Understanding Split helps in project planning and scoping
Understanding the split between frontend and backend helps clients plan projects more effectively and set realistic timelines and budgets. It also improves communication with development teams, making it easier to discuss features, changes, and priorities. By knowing what each side handles, clients can avoid misunderstandings, prevent scope creep, and make more informed decisions throughout the development process.
What to Consider When Building Your Project
When building a software project, it’s important to assess your specific needs to guide development. Consider whether your project is frontend-heavy (focused on user experience and design) or backend-heavy (driven by data processing, logic, or integrations). For example, a marketing landing page or a blog is usually frontend-heavy, requiring great design and responsiveness. A logistics dashboard or a finance app, on the other hand, is backend-heavy, with a focus on data, real-time updates, and integrations.
Determine if you’ll be using a CMS like WordPress for quicker deployment or opting for a custom-built platform tailored to your business logic. Also, think about whether you require features like real-time updates, interactive dashboards, or complex API integrations, as these will influence the architecture, timeline, and required expertise. Clear answers to these questions help define the scope and ensure your project is built on the right foundation.
Performance & Security: Why They Matter
When developing software, performance and security are just as critical as functionality and design.
A slow-loading frontend can turn users away, even if your backend is robust. Similarly, a well-designed UI is useless if the backend fails to protect user data or crashes under load.
Be sure your development team accounts for:
- Frontend performance: fast page loads, mobile responsiveness, image optimization
- Backend performance: optimized queries, efficient code, scalability under high load
- Security: user authentication, encrypted data transmission, secure APIs
Choosing the Right Development Partner
Selecting the right development partner is crucial for building a successful software product. Look for a team that has a deep understanding of both frontend and backend development, as this ensures they can deliver a seamless, functional, and user-friendly solution.
- Choose a team with strong frontend and backend expertise
Ensures a well-rounded, seamless software solution. - Prioritize cross-functional collaboration
Designers, developers, and strategists working together lead to better alignment and results. - Darosoft offers full-stack capabilities
From intuitive UIs to powerful backend systems, we handle end-to-end development. - Proven experience across industries
Our team helps businesses build scalable, custom solutions that align with their goals.
Wrapping up
Frontend and backend development are two sides of the same coin both are essential to building a successful software product. While the frontend shapes the user experience, the backend powers everything behind the scenes. The more you, as a client, understand this split, the more effectively you can plan, collaborate, and make informed decisions.